Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that is used as an umbrella term for a group of antioxidant chemicals.
Being a fat-soluble vitamin, it does not require to be replenished often and can be stored by our body for a long time.
This nutrient, as already mentioned is essentially an antioxidant that protects the cells inside the body from damages caused by free radicals and thus increases the overall lifespan of a cell.
Vitamin E naturally occurs in many foods and is recommended to be sourced naturally rather than supplementing it.
Apart from high antioxidant properties, vitamin E has also been shown to play a role in the human immune system and metabolism.
Due to its abundant availability and relatively low intake amount (recommended), vitamin E deficiency is very rare although some individuals have a higher risk of suffering from it than others.
In this article, we are going to be discussing vitamin E and exploring different corners and points of it on the way (as always). But very first look at Vitamin E deficiency symptoms.
Vitamin E deficiency
Vitamin E deficiency is pretty rare. This is because it is not required in a very large amount, can be stored in the body for a long time and there are plenty of sources to choose from. Most individuals will get their daily vitamin allowances through their diet.
Although it’s an uncommon condition, certain individuals with certain behaviors and conditions are prone to this deficiency. This includes people with a fat absorption problem, in which they cannot properly metabolize the fats; this can be a problem because vitamin E is to be taken with fatty food. This condition is termed as “fat-malabsorption”.
People with inherited conditions like cystic fibrosis or bile duct obstruction which resists them to absorb the vitamins efficiently are also automatically more prone to this deficiency. Along with that, if an individual has an abnormally functioning alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, then he/she will also be highly prone to vitamin E deficiency.
Premature babies can be underweight due to vitamin E deficiency.
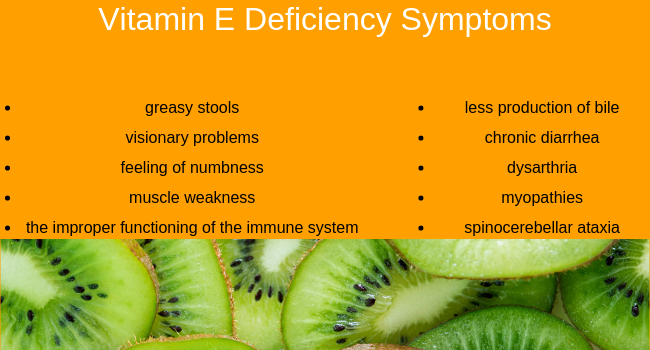
vitamin E deficiency symptoms
- greasy stools
- visionary problems
- feeling of numbness
- the improper functioning of the immune system
- muscle weakness
Serious symptoms of this deficiency are:
- less production of bile
- chronic diarrhea
- dysarthria
- myopathies
- spinocerebellar ataxia
What is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E (C29H50O2) is a term used to refer a group of antioxidants (8 to be specific) each of them having their own distinctive properties.
Also, read about
- Vitamin A|Benefits|Deficiency Symptoms|Source
- Vitamin D|Benefits|Deficiency Symptoms|Source
- Vitamin A to Z Brief Guide
And they are further divided into two sub-categories which are
Tocopherol (C29H50O2) (alpha, beta, gamma, delta)
Tocotrienol (C26H38O2) (alpha, beta, gamma, delta)
Both of those have four chemicals under them, which equates to 8 (in total). Together they are called tocochromanols.
Vitamin E is fat-soluble; this means that it has to be consumed with fatty food (because this type of vitamin dissolves in fat to work). It also means that it can be stored in our body for a relatively long period and doesn’t need to be replenished frequently.
This nutrient can’t be synthesized by us human beings and needs to be outsourced. Essentially vitamin E is synthesized in various plants from homogentisic acid.
Out of the different forms of vitamin E that we stated earlier, alpha-tocopherol holds a special significance. Out of the 8 known chemicals, alpha-tocopherol is what we human beings metabolize majorly.
This is because the other forms are mostly excreted out of the liver via faeces and alpha-tocopherol is the one which gets resecreted to the bloodstream hence increasing the concentration of it.
The reason be that alpha-tocopherol incorporates with the alpha-tocopherol transfer protein, which secretes the vitamin into the bloodstream.
Vitamin E benefits
- Vitamin E primarily functions as an antioxidant that protects cells in the body from damage inflicted by free radicals.
Free radicals are particles which contain “unshared electron” and are highly reactive. These particles are formed inside our bodies after a natural process like the conversion of food to energy.
These highly reactive particles then react vigorously with oxygen present inside to form reactive oxygen species or ROS.
These ROS particles can cause damage to the cells of the body, which can cause serious problems down the road. Antioxidants help cope with ROS and help protect the cells by neutralizing it.
Antioxidants are also known to clear artificially induced pollutants like smoke, which also brings in free radicals with it.
- Apart from that vitamin E is also been shown to help our body’s immune system and in our metabolic activities. It helps reduce the chances of an individual suffering from various cardiovascular diseases by neutralizing the free radicals.
- Vitamin E also improves the inner lining of the blood vessels, which makes the wall less sticky for the particles near it for a smooth flow.
- It encourages a protein called “Kinase C” to function more actively. This protein plays a role in smooth, platelets, muscle cells.
- Vitamin E also helps in the formation of red blood cells.
- Vitamin E protects from certain types of diabetes and vision impairments conditions by helping correct various retina related complications.
Vitamin E sources
There is a wide range of food products available when it comes to sourcing vitamin E. From nuts, green leafy vegetables, vegetable oils, and fortified foods. There are a lot of varieties to choose from.
Here are some of the best sources of vitamin E
Nuts and seeds:
- Almonds
- Sunflower seeds
- Peanuts
- Hazelnuts
- Peanut butter (fortified)
Fruits and Vegetables:
- Broccoli
- Tomato
- Spinach
- Mango
- Kiwi Fruit
Oils:
- Wheat germ oil
- Corn oil
- Soybean oil
- Sunflower oil